
Introduction
The Japan Warehouse Robotics Market size is predicted to reach USD 939.3 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 16.7%. Japan’s warehouse robotics market is at the forefront of global innovation in 2025, driven by the country’s advanced technological infrastructure, booming e-commerce sector, and strategic investments in automation. As part of the Asia-Pacific warehouse robotics market, projected to hold over 52.7% of the global market share in 2025, Japan is leveraging its robotics expertise to transform warehousing. This article explores the latest trends, developments, and challenges shaping Japan’s warehouse robotics landscape, drawing on recent industry insights and posts on X.
Japan’s Robotics Dominance
Japan has long been a global leader in robotics, with approximately 631 industrial robots per 10,000 manufacturing workers in 2021, a figure that has since increased. The warehouse robotics market benefits from this expertise, driven by key players like Daifuku Co., Ltd., FANUC Corporation, and Mujin. The country’s Society 5.0 initiative, which integrates digital technology with human capabilities, is accelerating automation adoption, particularly in logistics. Posts on X highlight Japan’s growing reliance on robotics to address labor shortages, with companies like Shenzhen Syrius Robotics planning to sell 3,000 units annually to Japanese firms, reducing staff needs significantly.
Key Developments in 2025
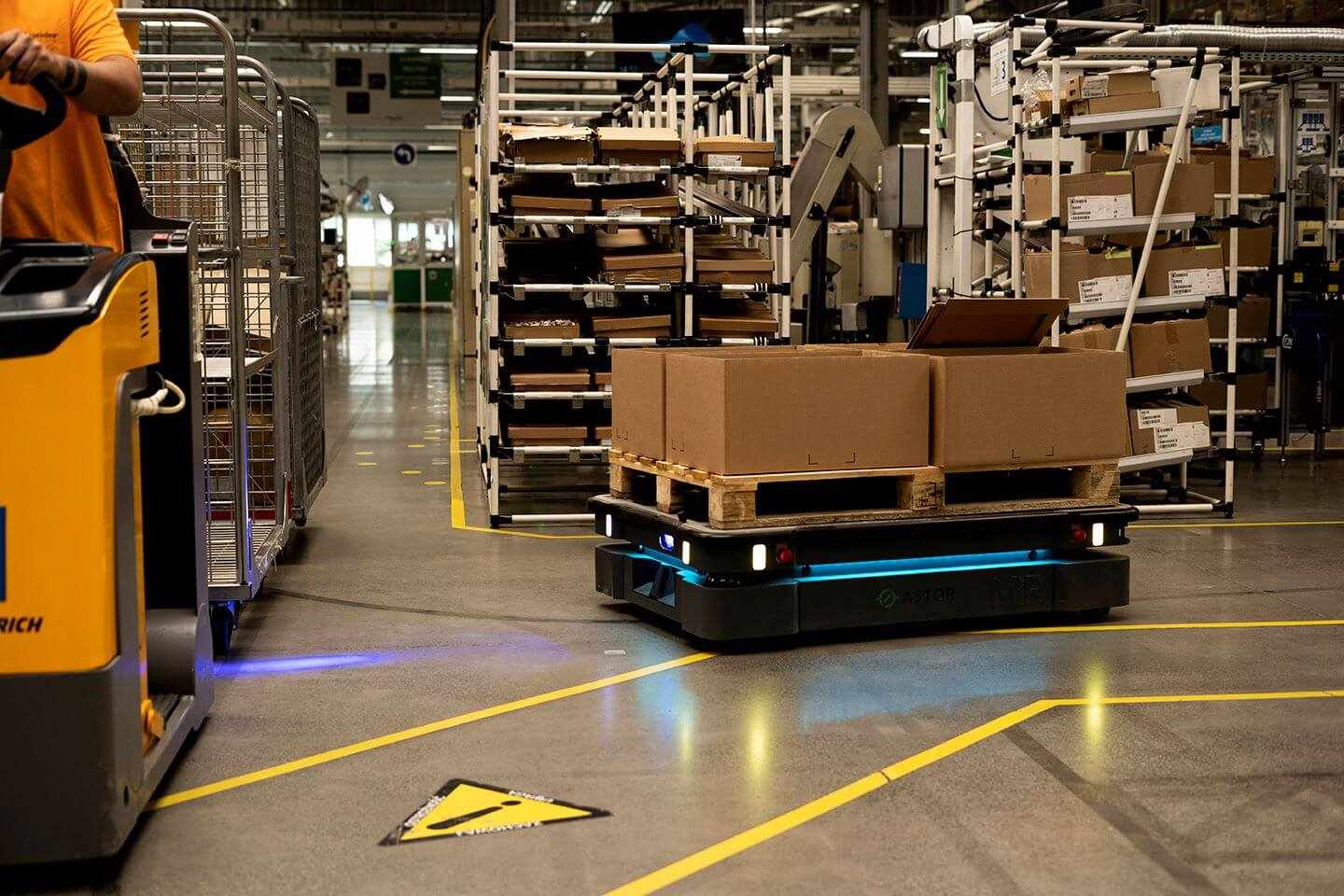
In 2025, Japan’s warehouse robotics market is witnessing significant advancements. Amazon’s deployment of its one-millionth mobile robot in a Japanese fulfillment center marks a global milestone, with the company’s DeepFleet AI model enhancing robotic efficiency. This reflects Japan’s role as a testing ground for cutting-edge automation.
Mujin, a Tokyo-based robotics firm, raised USD 85 million in its Series C funding round in 2024, aiming to launch fully autonomous robotic warehouses by 2025. These warehouses, powered by the MujinController platform, enable end-to-end automation, from picking to packing, revolutionizing logistics operations.
In May 2024, Intel announced a partnership with 14 Japanese companies to automate chipmaking processes, including packaging, with implications for warehouse robotics. This collaboration leverages AI and IoT to enhance robotic precision, aligning with Japan’s focus on smart warehousing.
Technological Innovations
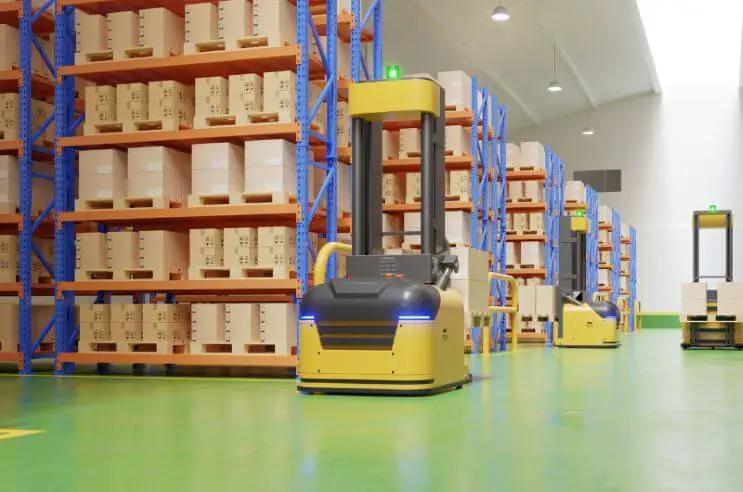
The integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT is driving Japan’s warehouse robotics market. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), holding over 29% of the global market share in 2025, are widely adopted for their flexibility in navigating complex warehouse environments. AI-powered robots dominate picking and placing functions, accounting for over 34% of the market share, optimizing order fulfillment and reducing errors.
The adoption of 5G enhances robot connectivity, enabling real-time data exchange and seamless navigation. Japan’s advanced 5G infrastructure supports this trend, with companies like FANUC integrating 5G into cobots for improved collaboration with human workers. Digital twins, virtual models of warehouse operations, are also gaining traction, allowing firms to simulate and optimize processes in facilities like Yokohama’s logistics hubs.
Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) models are making automation accessible to SMEs, with the global RaaS market projected to reach USD 8.4 billion by 2032. In Japan, this model supports retailers like Rakuten, enabling cost-effective adoption of robotics.
Drivers of Growth
Japan’s e-commerce sector, fueled by platforms like Rakuten and Amazon Japan, is a primary driver, accounting for 25.8% of the global warehouse robotics market share. The need for rapid delivery in urban centers like Tokyo and Osaka is pushing companies to invest in robotics. Labor shortages, exacerbated by Japan’s aging population, are another catalyst, with robotics reducing manpower needs by up to 30%.
The food and beverage and consumer electronics sectors, relying on robots with payload capacities below 20 kg, hold over 26% of the market share, driven by the need for precision in handling fragile goods. Government initiatives like Society 5.0 and investments in smart infrastructure further support adoption, aligning with Japan’s focus on sustainability and efficiency.
Challenges
Despite its leadership, Japan’s warehouse robotics market faces challenges. High initial costs, even with RaaS, pose barriers for SMEs. Integrating robotics with legacy systems requires significant investment in training and infrastructure. Cybersecurity risks, with global hacking losses reaching USD 2.1 billion in 2025, highlight the need for secure robotic systems. Additionally, regulatory compliance, such as adherence to Japan’s APPI data privacy laws, adds complexity to AI-driven robotics deployment.
Industry and Regional Impact
Tokyo, Osaka, and Yokohama are key hubs for warehouse robotics, driven by their logistics infrastructure and proximity to major ports. The e-commerce sector leads adoption, followed by food and beverage and electronics. Amazon’s milestone in Japan underscores the country’s role as a global logistics innovator. Robotics adoption is also creating jobs in tech development and maintenance, supporting economic growth.
Conclusion
Japan’s warehouse robotics market is thriving in 2025, leading global innovation through its advanced technological ecosystem, e-commerce growth, and strategic investments. Innovations like AMRs, AI integration, and RaaS models, coupled with milestones like Amazon’s millionth robot and Mujin’s autonomous warehouses, position Japan at the forefront of smart logistics. Despite challenges like high costs and cybersecurity risks, government support and a focus on sustainability ensure continued growth. As Japan drives the global warehouse robotics market, it is setting a benchmark for efficiency and innovation by 2032.













Write a comment ...